Describe the Role of the Placenta in Fetal Development
These cells are vital for the fetus nutrition. They also disappear from the chorionic plate.
It supports the developing foetus in utero by supplying nutrients eliminating waste products of the foetus and enabling gas exchange via the maternal blood supply.

. It connects the mother to the fetus through the umbilical cord and carries out the functions your fetus cannot perform by itself 2. Placental lactogen stimulates the development and secretion of the mammary gland. Human chorionic somatomammotropin HCS also known as human placental lactogen HPL promotes breast development and alters the metabolism of the mother.
As 5-ht has been shown to af- fect neuronal proliferation and axonal outgrowth during this period the placenta could provide substrates regulating brain development 18. This lecture is an introduction to the development and functions of the placenta. Development of the placenta After the 4th month the cytotrophoblast slowly disappears from the walls of the tertiary villi interactive diagram whereby the distance between the maternal and fetal vessels diminishes.
Progesterone serves the synthesis of fetal corticoids and participates in the formation of decidual cells in the uterus. The placenta is an organ responsible for providing oxygen and nutrients and removing waste substances. This organ provides oxygen nutrients during pregnancy and filters foetal waste.
The functions of the placenta are many. The placenta has numerous responsibilities. The following are the roles played by the placenta during pregnancy.
State the role of placenta in the development of embryo. The placenta plays an absolutely crucial and essential role during the nine months of pregnancy. By the end of pregnancy the umbilical cord is approx.
The first and most important function of placenta is delivering oxygen to your baby and removing carbon dioxide from used oxygen. Via the umbilical cord and the chorionic villi this organ delivers blood nutrients and oxygen to the developing fetus. Together these studies suggest that the traditional view of the placenta as a passive site of transport of maternal nutrients growth factors and hormones needs to be expanded to include a role in supporting CNS development through adaptive responses to the maternal environment.
The placenta is an amazing organ. The role of the placenta in fetal nutrition and growth. You breathe and the oxygen you take in goes to the placenta through your blood.
It mediates the active transport of nutrients and metabolic wastes across the barrier separating maternal and fetal compartments as well as modifying the composition of some nutrients through its own metabolic activity. The placenta a mateno-fetal organ which begins developing at implantation of the blastocyst and is delivered with the fetus at birth. It also plays an important role in hormone production and it protects the foetus from bacteria and infections.
The Placenta The placenta serves as a medium that helps in extracting nutrition from the mother and providing it to the growing fetus. Additionally the placental growth factor promotes fetal development and maturity. The umbilical cord connects the fetus with the fetal part of the placenta chorionic plate.
5-ht is also reported to play a central role in the maturation of circuits that modulate emotional function in mice 19 and polymorphisms in genes related to 5-ht function. The 3 rd week of embryonic development. Easy Solution Verified by Toppr The important role of placenta is to provide nourishment to the developing embryo as well as it plays important role in the exchange of gases between the embryo and mother.
It also stimulates the growth of fetal organs and the weight of the placenta. The placenta plays a vital role in maternal-fetal physiology. The placenta plays a key role in the nutrition of the fetus.
Fetal Consequences of Perturbations in Maternal Metabolism. Solve any question of Human Reproduction with- Patterns of problems. A fully developed placenta is made up of a large mass of blood vessels from both the mother and fetus.
Placenta The placenta is a temporary organ that begins to form from the trophoblast layer of cells shortly after implantation. Over time the villi develop increasingly dense branching to accommodate the increased demand of the developing fetus. It is made of the cells that are derived from the mother and foetus.
It is then connected to the fetus by the means of an umbilical cord. Functions Of The Placenta During Pregnancy. The placenta may also contribute to fetal programming with health.
The placenta is your unborn babys life support system and plays a key role in its development. It typically attaches centrally to the chorionic plate of the placenta. The placenta Greek plakuos flat cake named on the basis of this organs appearance.
Since your baby does not breathe yet the placenta does this work. The placenta performs myriad functions to support fetal development including facilitating blood flow gas exchange waste elimination and serving as a protective barrier for the fetus against any infections the mother experiences during pregnancy. It grows into the wall of the uterus and is joined to the fetus by the umbilical cord.
Existing evidence implicates the placenta as the origin of some common pregnancy complications. 10 rows The placenta a mateno-fetal organ which begins developing at implantation of the blastocyst and. The placenta develops to bring oxygen and nutrients to the fetus and to move harmful waste and nutrients away.
The development of the umbilical cord begins at approx. The placenta continues to develop and grow to meet the needs of the growing fetus. The placenta is a vital connecting organ between the maternal uterus and the foetus.
The placenta is defined as the organ that is found in mammals during the development of the foetus. Not only does it play avitalroleinthedeliveryofnutrientsandoxygentothe growing fetus but also it contributes significantly to the hor-monalmilieuofbothmotherandfetusduringpregnancyThe word placentaoriginates from the Greek word plakoenta meaning flat slab-like object. It is a disc shaped or pancake shaped fleshy organ that is attached to the walls of the uterus.
One of the main functions of the placenta is to allow oxygen in the maternal blood to move into the fetal vessels and carbon dioxide in the fetal blood to diffuse into the mothers blood system. The placenta and its health are vital to the health of a womans pregnancy and foetal development. Moreover some maternal conditions such as inadequate nutrition diabetes and obesity are known to adversely affect placental function with subsequent negative impact on the fetus and newborn.
In this article we shall look at the development of the placenta. Only recently have we begun to understand. The materials between the mother and the foetus are exchanged with the help of the placenta.
The placenta extracts the oxygen and puts in into your babys blood.

Human Embryogenesis Embryonic Development Anatomy And Physiology Physiology
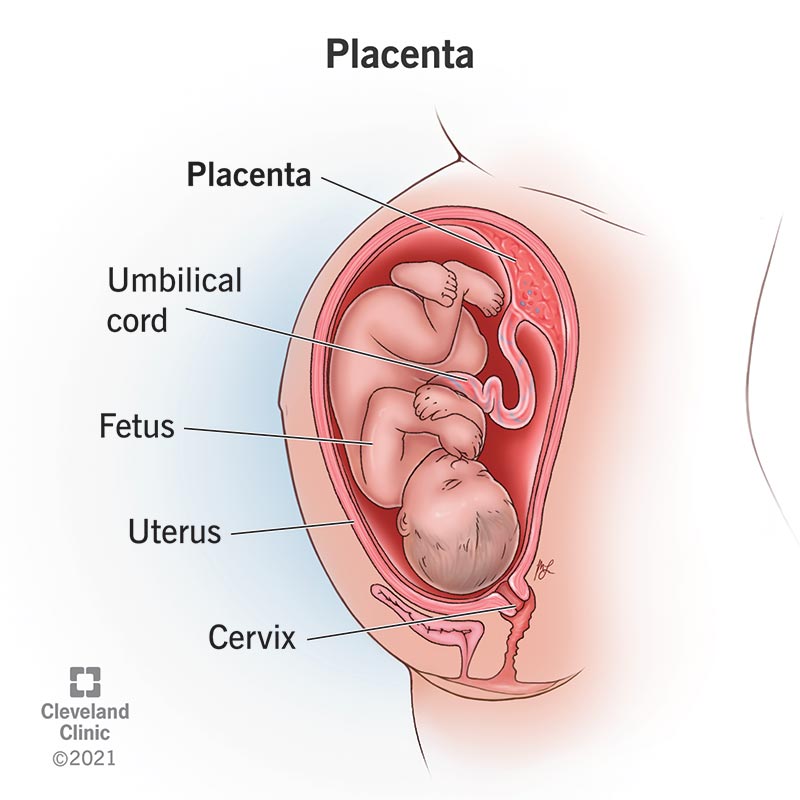
Placenta Overview Anatomy Function Complications

Placenta Development Human Placenta Female Reproductive System Anatomy Placental

Placental Insufficiency What Is It Causes Symptoms Treatment And More Osmosis
No comments for "Describe the Role of the Placenta in Fetal Development"
Post a Comment